A Guide to Using Google NotebookLM for Course Design
Google NotebookLM is a powerful tool for organizing and developing course content and can enhance and fine-tune your existing ideas.
What is Google NotebookLM?
Google NotebookLM allows users to easily create, organize, and share notes. It acts like a virtual assistant that uses existing information to summarize details, clarify complex ideas, and generate relationships based on selected sources. It can handle various content types, including text, images, graphs, and diagrams.
Benefits of Using Google Notebook LM for Course Design
Organized Planning
Instructors can create separate notebooks for course outlines, reading materials, assessment plans, study guides, and course lectures. This organized structure simplifies the planning process and allows for easy navigation and access in the future.
Resource Compilation
It allows you to compile links, articles, videos, and other materials in one place. You can save links directly into your notebook, annotate them for future reference, and classify them according to topics.
Collaborate
It supports collaboration by allowing multiple users to edit and comment on notes in real time.
Easily Accessible
Since Google NotebookLM is cloud-based, you can access your notes anytime, anywhere, and on any device, allowing you to brainstorm ideas anywhere!
How to get started with Google NotebookLM
Let me walk you through how to start Google NotebookLM!
Creating a Notebook
Go to https://notebooklm.google.com/ and login with your Gmail account.
You will see your Google NotebookLM Dashboard with all the different notebooks you have created so far.
To create a new Notebook select "Create New"
Adding Content to your Notebook
It will prompt you to upload documents, google drive files, text, audio files, website links and YouTube videos. If you are not ready to do that, you can click on the X to close the window.
Make sure to name your Notebook.
Summarizing content using NotebookLM
Once you have uploaded all the content you want for the specific Notebook you created, you can use the "Chat" feature to ask questions about the different content. You can easily select the content you want to include by checking or unchecking the corresponding boxes next to each item. NotebookLM also offers you prompts to choose from, making it easier to develop your content. Please note: Content might not be accurate, so make sure to check for any mistakes.
How to Use Google Notebook LM for Course Design
Google NotebookLM is a powerful tool for organizing and developing course content and can enhance and fine-tune your existing ideas. You can use Google Notebook LM as a starting point for your course content. It will provide a solid foundation for you to build upon the ideas and suggestions it offers to make them even better and more tailored to your specific needs.
Create Course Objectives: create course or module objectives based on selected content. You can enter prompts like, “Create objectives for a module on [topic]” to get customized suggestions.
Develop Lesson Plans: outline the main concepts for each lesson. For instance, input, “Create a lesson plan for teaching [specific topic], including objectives, materials, and activities.”
Create Study Guides: use prompts like, “Create a study guide for [topic] that includes key concepts and questions.” NotebookLM can help summarize important information and develop study questions.
Create Discussion Prompts: generate discussion prompts based on content selected. You can input, “What are some engaging discussion prompts for [topic]?” to stimulate thoughtful discussions in class.
Create Rubrics and Criteria: determine what you will assess (e.g., projects, participation, etc.). Input requests along the lines of, “Create a rubric for assessing [specific project or assignment] that includes criteria for [aspects such as creativity, understanding, effort, etc.].” This will produce a structured assessment guide that you can further customize.
You can effectively use Google NotebookLM to streamline your course design process, enhance student engagement, and collaborate with others in the educational field! Happy designing!
Optimizing Learning Objectives with AI
With the increasing integration of AI (Artificial Intelligence) into the educational landscape, instructors can now use AI for content creation, such as developing clear learning objectives and assessments.
With the increasing integration of AI (Artificial Intelligence) into the educational landscape, instructors can now use AI for content creation, such as developing clear learning objectives and assessments. Well-defined learning objectives clarify expectations for students and ensure that assessments are closely aligned with those goals.
In this blog post, we'll take a look at some helpful AI tools for developing course objectives and walk you through the process of creating them.
Understanding Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives are important parts of any course. Learning Objectives communicate to students what the instructor expects and what the course accomplishes. Learning objectives are good practice and make for a well-designed course.
How Can I use AI in Creating Learning Objectives?
Alignment with Standards
Ensure learning objectives align with accreditation requirements or educational benchmarks. This helps maintain credibility and relevance in course offerings.
Feedback and Iteration
Provides suggestions for improving learning objectives based on student feedback or performance data. Continually improving course objectives helps them remain current and impactful.
Analyzing Learning Outcomes
Analyze existing course materials to identify important outcomes. By processing large volumes of data, AI can suggest relevant knowledge and skills that should be included in your objectives.
Generate Content
Generate initial drafts of learning objectives based on input from instructors. Instructors can focus more on refining content rather than starting from scratch.
AI Tools to Use to Create Learning Objectives
ChatGPT - AI chatbot that can generate human-like responses to different prompts
Google Gemini - Helps to write, plan and learn and responds with information it already knows or from other sources
Grammarly - Uses AI to enhance your writing and offers personalized guidance
Claude AI - Can generate human-like responses to text or image inputs.
Microsoft Copilot - Allows you to generate text or create images based on text prompts
Incorporating AI into Your Learning Objectives
To get started with using AI for creating course objectives, follow these steps:
Determine Course Themes: What is the primary focus of your course? What learning outcomes can students anticipate? For instance, if your course is in Environmental Science, consider whether your central theme revolves around sustainability.
Select the Appropriate Tool: Select one or more AI tools that best fit your needs. Take time to explore their features to see if they can assist you in aligning and generating objectives.
Draft Objectives: Use AI to generate preliminary course objectives. Make sure to refine the objectives with your insights and expertise.
Seek Feedback: Share your objectives with colleagues for feedback. AI can assist in analyzing this feedback to improve your objectives.
Align and Finalize: Ensure the objectives align with your teaching strategies and assessment methods before finalizing them.
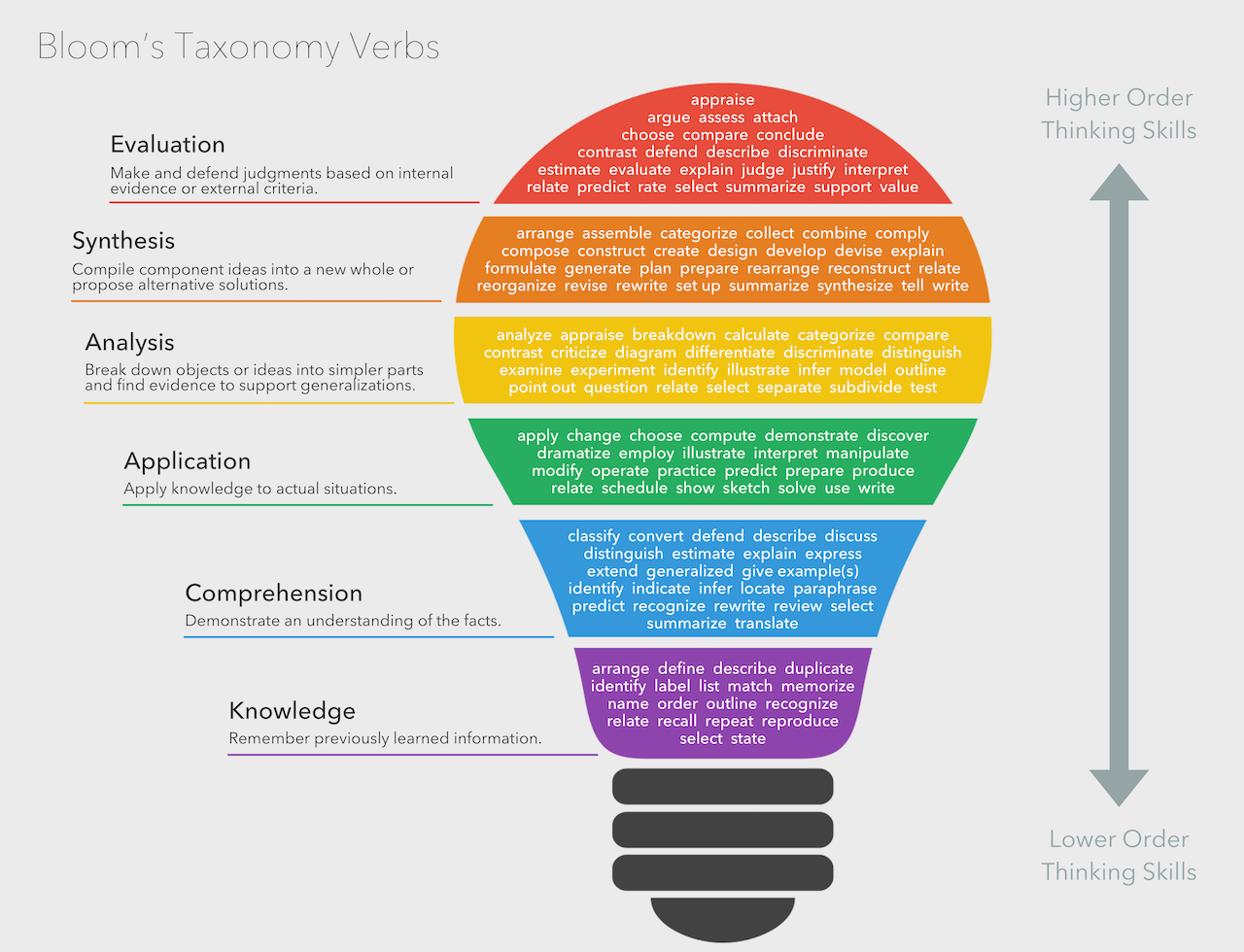
Bloomy Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs by Fractus Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Verbs in Bloom's Taxonomy are measurable and help instructors create quantifiable assignments and assessments. These verbs are helpful in planning lessons and curriculum.
AI will help you to:
Understanding Bloom's Taxonomy: Clear explanations of the different levels of Bloom's Taxonomy.
Generate Action Verbs: Suggest specific action verbs associated with each level of Bloom's Taxonomy, helping instructors create precise and measurable learning objectives.
Customizing Objectives for Students: Analyze student data and suggest customized learning objectives that meet varied learning styles and levels of understanding.
Providing Examples: Generate examples for learning objectives based on the subject area and educational goals, serving as a starting point for educators to refine as they see fit.
Facilitating Alignment: Aligning learning objectives with curriculum standards, assessments, and instructional strategies.
Feedback: Offers constructive feedback on drafted objectives, suggesting improvements and revisions to enhance clarity and effectiveness.
Sample Prompts for AI to Generate Course Level Objectives
Generate a list of course objectives for a [Subject/Topic] course aimed at [Target Audience]
What are some measurable learning objectives for a [Course Title] focused on [Key Theme/Concept]?"
Create detailed learning objectives for a lesson on [Specific Topic] that align with [Educational Standard or Framework]
What are three learning objectives for a unit on [Topic/Skill] for students in [Grade Level or Course Type]?
Suggest learning objectives using action verbs from Bloom's Taxonomy for a course on [Subject]."
How can I formulate objectives at the [Choose Level: Remembering, Understanding, Applying, etc.] level for a course about [Topic]?"
What learning objectives can I use to ensure my course on [Topic] is aligned with [State/National Standards]?"
Analyze the following draft objectives for clarity and effectiveness: [insert your draft objectives]. What improvements can you suggest?"
What revisions can enhance these learning objectives for a course on [Topic]? [insert your objectives]
AI provides solutions to create meaningful course objectives. Embracing AI in education saves time and empowers instructors to focus on delivering high-quality learning experiences. So why not take advantage of these advancements and elevate your course design today?
The Power of Social Learning: How to Incorporate Social Learning in Your Classroom
People learn by watching other people. Social learning theory states that we learn from anyone we come in contact. Humans can learn from anyone, including family members, coworkers, and celebrities!
People learn by watching other people. Social learning theory states that we learn from anyone we come in contact. Humans can learn from anyone, including family members, coworkers, and celebrities! The same concept can be applied in education. Students learn through social interactions with other students. As students interact with one another, they also learn from each other.
We will explore how you can use social learning in your teaching strategy.
Social Learning Benefits
Retention: when learners discuss how they have applied what they have learned with each other, this helps to enhance content retention.
Participation: learners interacting with each other helps improve learning and increases participation.
Collaboration: improves collaboration by allowing learners to collaborate and share ideas.
Expanded perspectives: can expand learners' perspectives by exposing them to different viewpoints and experiences.
Way to Incorporate Social Learning in Your Class
Use social media!
Learners can connect to do assignments, share resources, or discuss topics.
X (formerly known as Twitter) - students can research different topics by using hashtags or keywords
LinkedIn - students can research different topics, create a LinkedIn group for students to learn from each other, or create their profile and build their network.
Facebook - create discussion topics so students can communicate with each other and the instructor. You can also use it to send messages or reminders.
Online Discussion Forums
Online discussion forums can be used to facilitate social learning. Learners can ask questions, share ideas, and collaborate with each other. You can use the discussion tool in your Learning Management System, like Canvas or Blackboard, to encourage student communication and collaboration.
Benefits of discussion forums:
creates a community
encourages classroom participation
allows students to contribute better to the discussion by giving them time to formulate their responses
Group projects
Learners can work together to complete a project and learn from each other. Students can share ideas, collaborate, and build on each other's strengths by working in groups.
Benefits of Group projects:
Encourages students to take ownership of their learning and develop essential communication, problem-solving, and time-management skills
Helps students develop a sense of community and belonging within the classroom, which can improve the overall learning experience
Peer Review
Learners can review each other's work and provide feedback, enhancing learning and collaboration.
Benefits of Peer Review:
Encourages learners to engage with and critically evaluate each other's work can help them identify gaps in their understanding and deepen their knowledge
It can help learners develop critical thinking skills by requiring them to evaluate and analyze each other's work, which can help them develop the ability to assess arguments and make informed decisions
Sample Peer Review Assignments:
Essay peer review - students can be assigned to read and provide feedback on each other's essays
Group project peer review - students working on a group project can be asked to provide feedback on each other's contributions and overall performance within the group.
Presentation peer review - students can be assigned to watch and evaluate each other's presentations.
Code review - for computer science or programming courses, students can be assigned to review each other's code and provide feedback on style, readability, and functionality.
Mentorship
Learners can be paired with a mentor who can provide guidance and support.
Benefits of Mentors:
improved grades - guide students on test-taking strategies
increased self-esteem - having someone who believes in them will make them more confident in their abilities
creates a feeling of community - introduces students to new experiences and ideas and to people who share similar interests
increased connection at school
career guidance - support students in their careers by providing them with job search strategies and networking opportunities
Social learning allows your students to engage more with you and each other, creating more communication and collaboration, leading to more memorable learning experiences. Creating a sense of community is important for supporting learning, especially in online or remote teaching environments.
Effective Course Design with the ADDIE Model
When designing a course, the most important part is ensuring the course is effective and meets the learners' needs. The ADDIE model of instructional design is commonly used for course design to create instructional materials and experiences that are well-organized, engaging, and meet the course learning objectives.
When designing a course, the most important part is ensuring the course is effective and meets the learners' needs. The ADDIE model of instructional design is commonly used for course design to create instructional materials and experiences that are well-organized, engaging, and meet the course learning objectives.
The ADDIE model consists of five phases: analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation.
Let's review how using these five phases will help design your course!
Analysis
During the analysis phase, you identify the learners' needs and determine your course's goals. This also includes analyzing who your audience will be, the learners' learning styles, and identifying potential learning barriers.
For example, some questions you can ask yourself will be:
What do you learners need to learn?
Do your learners need to know specific skills to take your class? Are there any technical requirements necessary for the class?
How will the class be structured? Do you plan to use weekly modules or by chapter?
How will you assess your learner's performance?
How do you envision their learning environment, and how will this affect their learning?
What kind of content will you be designing to engage your learners? For example, will you use graphics, videos, text, or audio?
This phase helps you understand your course needs and how you will measure success.
One way to achieve this is to use the backward design model to identify the learners' needs and determine your course's goals. The backward design model helps you to start with the end goal in mind, which is the desired learning outcomes, and then work backward to create instructional materials and activities that will enable learners to achieve those outcomes.
You can identify what learners need to learn, what skills they need to acquire, and how you will measure their learning outcomes. You can also identify potential learning barriers and determine how to overcome them.
For example, if you are designing a course on project management, you can start with the end goal of the course, which is for learners to be able to manage projects successfully. Then, you can work backward to identify the specific skills and knowledge learners need to acquire to achieve that goal. You can also identify the best instructional materials and activities to enable learners to acquire those skills and knowledge. Lastly, you can determine how to assess the learning outcomes and address any potential obstacles preventing learning.
Design
In this phase, you will create a course outline that includes the following:
Learning objectives - for your course and modules
Course materials - content, videos, and audio or other course materials will you be designing for your course or plan to use
Assessments - assignments, quizzes, projects, or other assessment methods will you be using to measure learning outcomes.
For example, a graphic design instructor might design learning objectives that include learning how to use design software, understanding design principles, and applying them to real-life design projects. The graphic design instructor will use video tutorials to teach learners about design software and hands-on design projects to apply the concepts learned in the course. The instructor will also use quizzes to test the learners' understanding of design principles and assess whether or not they can apply what they have learned to real-life design challenges.
This phase is also where you will decide the most effective delivery methods for the course, such as face-to-face or online instruction.
Development
The development phase is where the actual course materials are created. This phase includes developing course content, creating multimedia elements such as videos or audio, and assessments. During this phase, you must ensure that you create course content accessible to all learners, regardless of their abilities.
For example, a photography instructor during this phase will create course content that consists of videos, audio, and different assessments to ensure that our learners have a well-rounded understanding of photography.
The content will also be accessible to all learners. The instructor will use closed captions in their videos to ensure that learners who are hard of hearing or deaf can still understand the content. He will also provide transcripts of the audio lectures for learners who prefer to read the content. Lastly, he will make sure that course content meets accessibility standards, which include providing alt tags for images and making sure that any external website used in the course can navigated by learners who use assistive technologies.
The photography instructor will create various materials for course content to engage the learners and cater to different learning styles. For example, he will develop interactive quizzes to test learners' knowledge of photography concepts and provide hands-on exercises to allow learners to practice their photography skills. The instructor will also create video tutorials that demonstrate specific techniques and provide examples of how to apply these techniques in real-life situations.
Implement
After developing the course, it is time to implement it. During this phase, the instructor delivers the course to the learners who take the class. Any necessary adjustments are made based on feedback from learners and instructors.
For example, a history college instructor recently developed an online course for their students. The professor implements it by giving their students access to the course materials. As the students go through the course, the professor receives feedback regarding the content, the format, and any technical difficulties they may have experienced. The professor uses this feedback to adjust the course, improve the experience, and meet the needs of the students. For example, most students need help understanding a particular module. In that case, the professor may create additional resources or provide more detailed explanations to help the students better understand the material. Similarly, if there are technical issues with the learning platform, the professor may work with the IT department to resolve them and improve the overall user experience. By making these necessary adjustments, the professor ensures that the course is effective and engaging for their students.
Evaluation
Lastly, the evaluation phase is where the success of the course is evaluated. In this phase, you want to analyze how effective the course materials were, the learner's performance in the class, and identify any areas for improvement.
For example, if you were a high school physics teacher who recently designed and implemented a new course on electromagnetism. You would collect student data and feedback during the evaluation phase to determine the course's effectiveness.
Some ways to collect feedback is to use surveys that ask questions such as:
Did you find the course materials engaging and useful?
Were the learning objectives clear and achievable?
Did the assessments accurately measure your understanding of the material?
Were you able to apply the concepts learned in the course to real-life situations?
How can the course be improved?
Based on the feedback collected during the evaluation phase, you can identify areas for improvement and make necessary changes to the course to help future students have an even better learning experience.
In conclusion, by following the ADDIE model, course designers can ensure that their courses are effective and meet the needs of learners.
Virtual or Augmented Reality in Instructional Design: A Guide for Educators
The world of instructional design is constantly evolving, and virtual or augmented reality (VR/AR) is one of the latest trends in the field. Both of these technologies allow users to engage in immersive learning experiences and allow for some exciting possibilities for learning different content.
The world of instructional design is constantly evolving, and virtual or augmented reality (VR/AR) is one of the latest trends in the field. Both of these technologies allow users to engage in immersive learning experiences and allow for some exciting possibilities for learning different content.
Difference between VR and AR
Virtual Reality allows the user to immerse themselves in a computer-generated environment that appears natural. In comparison, Augmented Reality provides a real-world experience of visual elements, sounds, or sensory stimuli delivered through cutting-edge technology. Both have unique benefits and challenges in instructional design.
Let's go over these benefits and challenges.
Learning Objectives
VR/AR can be a powerful tool for creating an engaging and enjoyable learning experience. However, it's important to consider whether the technology is being used to support the course's learning objectives or simply using it for the sake of using it. It should also aid in providing students with hands-on experience and a better understanding of complex concepts.
VR/AR platforms
Various VR/AR platforms are available, from simple mobile apps to complex headsets. Choose the platform that best suits your learning objectives and budget. For example, Adobe Aero allows you to create immersive AR without coding, which is excellent for beginners. Adobe Aero will enable you to add 2D images from Adobe Photoshop or Illustrator. Another example is Google Tilt Brush which is great for artists and a great VR design software. It allows you to paint in 3D using different brushes and interact and walk around your artwork.
Realistic Scenarios
The latest AR/VR technologies are revolutionizing how students learn and explore. With immersive learning experiences, students can now travel through time and witness historical events firsthand or explore the human body in remarkable detail. These state-of-the-art tools are opening up a whole new world of possibilities for education.
The power of VR/AR lies in its ability to create realistic, immersive scenarios that textbooks cannot offer. Learners can hone their real-world skills in a secure and structured setting. Whether it's hands-on training or simulated scenarios, these experiences can help learners gain confidence and expertise without the risks associated with real-life situations.
For example, you can create VR scenarios such as medical procedures or visiting Michelangelo's David in the Galleria dell'Accademia without flying to Italy. You can also use AR overlays to view the night sky. For example, SkyView allows students to view the universe and identify stars and planets.
Challenges of using AR/VR
It's worth noting that AR/VR technology can come with some challenges. For starters, it can be quite costly and requires a fair amount of technical resources to maintain. Additionally, some users may experience fatigue or anxiety when using AR/VR due to the high cognitive demand placed on them. It's also important to acknowledge that while AR/VR can be affordable to use in some instances, there are, unfortunately, some educational organizations that may require assistance to be able to afford this technology.
Support and feedback
VR/AR can disorient some learners, so providing clear instructions and feedback is important throughout the experience. Ensure learners know what they are expected to do and allow them to give feedback on their experience. With feedback, you will be able to gauge the effectiveness of the technology.
To sum up, implementing AR/VR technology in education can revolutionize how students learn by providing immersive, lifelike experiences that translate into improved comprehension and retention of critical concepts.
ANATOMY OF A LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Learning Objectives are essential parts of any course module and course.
Designing your online course is not merely about creating content and sharing your passion for the subject you are teaching. You also need to make sure that what you are teaching is being learned. How do you ensure that this happens?
Learning Objectives are essential parts of any course module and course. Learning Objectives communicate to the student what they will learn after completing a learning module and be confident they will make measurable progress. They also help define what the instructor expects of them for the particular lesson and what the course accomplishes. Learning objectives in each of your course modules are good practice and make for a well-designed course.
When designing your learning objectives, you should ask yourself the following questions:
What will the students be learning?
What level of thinking will be used to process the content?
What observable student behavior will serve to show that the student has learned what they are supposed to?
What are the conditions (materials, time limits, etc.) that the student will expect to work under?
What is the level of mastery? What will satisfy you?
Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs by Fractus Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Created in 1956 by Psychologist Benjamin Bloom, Bloom’s Taxonomy is the most extensively used scale to demonstrate the level of expertise required for measurable student outcomes. Verbs in Bloom’s Taxonomy are measurable and help instructors create assignments and assessments that are quantifiable. These verbs are useful in planning lessons and curriculum.
There are six levels of knowledge in Bloom’s Taxonomy:
Knowledge -is measured by asking questions to see what they have remembered from a lesson—for example, a multiple-choice test.
Comprehension – determines their level of understanding by asking students to summarize, describe or discuss a topic.
Application – students apply what they have learned in real-life situations.
Analysis -students analyze a problem and provide supporting evidence as to how they solved the problem.
Synthesis – students merge information they have learned to provide new ideas and solutions.
Evaluation – students use the knowledge they have acquired to evaluate and apply their learning using evidence, observations, and other criteria determined by the student.
Bloom’s Taxonomy by Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Generic license.
Remember -is measured by asking questions to see what they have remembered from a lesson—for example, a multiple-choice test.
Understand – determines their level of understanding by asking students to summarize, describe or discuss a topic.
Apply – students apply what they have learned in real-life situations.
Analyze -students analyze a problem and provide supporting evidence as to how they solved the problem.
Evaluate – students use the knowledge they have acquired to evaluate and apply their learning using evidence, observations, and other criteria determined by the student
Create – students merge information they have learned to provide new ideas and solutions.
Let’s break it down!
Sample Objectives
Sample 1: Learning Objective (Text)
Students will be able to draw on Sketchpad the four life cycles of a butterfly after reading The Very Hungry Caterpillar.
Conditions – Sketchpad, reading The Very Hungry Caterpillar
Cognitive Process – draw (Remember) (Knowledge)
Content – life cycles of a butterfly
Observable Proving Behavior – drawing on Sketchpad the life cycles of a butterfly
Standard of Mastery – drawing the four life cycles of a butterfly
Sample 2: Learning Objective (Text)
After a lesson on Linear Algebra, students will be able to correctly solve at least 8 out of 10 algebra problems using Linear Algebra.
Conditions – lesson on Linear Algebra
Cognitive Process – solve (Apply) (Application)
Content – Linear Algebra
Observable Proving Behavior – correctly solve algebra problems using Linear Algebra
Standard of Mastery – at least 8 of 10 Linear Algebra problems
Sample 3: Learning Objective (Text)
Given the website, Linkedin.com and Chapter 4 in their textbook, students will create a Linkedin profile to effectively navigate the Linkedin interface and assess how Linkedin can be used to connect with peers and professional networking activities.
Conditions – Linkedin website, Chapter 4 of textbook
Cognitive Process – create (Create) (Synthesis)
Content – assess how Linkedin can be used to connect with peers and professional networking activities
Observable Proving Behavior – Linkedin profile
Standard of Mastery – effectively navigate the Linkedin profile
Objective Builder
Developed by the University of Central Florida , use the Objective Builder Tool and create your objectives with this easy-use tool!
While it can be a bit daunting creating learning objectives, correctly done objectives are the first step in creating a high-quality course module and instruction.
What difficulties have you encountered creating learning objectives? Hopefully, this post has provided helpful information! Please let me know what other topics you would like for me to discuss in the comments below. See you in the next post!