Optimizing Learning Objectives with AI
With the increasing integration of AI (Artificial Intelligence) into the educational landscape, instructors can now use AI for content creation, such as developing clear learning objectives and assessments.
With the increasing integration of AI (Artificial Intelligence) into the educational landscape, instructors can now use AI for content creation, such as developing clear learning objectives and assessments. Well-defined learning objectives clarify expectations for students and ensure that assessments are closely aligned with those goals.
In this blog post, we'll take a look at some helpful AI tools for developing course objectives and walk you through the process of creating them.
Understanding Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives are important parts of any course. Learning Objectives communicate to students what the instructor expects and what the course accomplishes. Learning objectives are good practice and make for a well-designed course.
How Can I use AI in Creating Learning Objectives?
Alignment with Standards
Ensure learning objectives align with accreditation requirements or educational benchmarks. This helps maintain credibility and relevance in course offerings.
Feedback and Iteration
Provides suggestions for improving learning objectives based on student feedback or performance data. Continually improving course objectives helps them remain current and impactful.
Analyzing Learning Outcomes
Analyze existing course materials to identify important outcomes. By processing large volumes of data, AI can suggest relevant knowledge and skills that should be included in your objectives.
Generate Content
Generate initial drafts of learning objectives based on input from instructors. Instructors can focus more on refining content rather than starting from scratch.
AI Tools to Use to Create Learning Objectives
ChatGPT - AI chatbot that can generate human-like responses to different prompts
Google Gemini - Helps to write, plan and learn and responds with information it already knows or from other sources
Grammarly - Uses AI to enhance your writing and offers personalized guidance
Claude AI - Can generate human-like responses to text or image inputs.
Microsoft Copilot - Allows you to generate text or create images based on text prompts
Incorporating AI into Your Learning Objectives
To get started with using AI for creating course objectives, follow these steps:
Determine Course Themes: What is the primary focus of your course? What learning outcomes can students anticipate? For instance, if your course is in Environmental Science, consider whether your central theme revolves around sustainability.
Select the Appropriate Tool: Select one or more AI tools that best fit your needs. Take time to explore their features to see if they can assist you in aligning and generating objectives.
Draft Objectives: Use AI to generate preliminary course objectives. Make sure to refine the objectives with your insights and expertise.
Seek Feedback: Share your objectives with colleagues for feedback. AI can assist in analyzing this feedback to improve your objectives.
Align and Finalize: Ensure the objectives align with your teaching strategies and assessment methods before finalizing them.
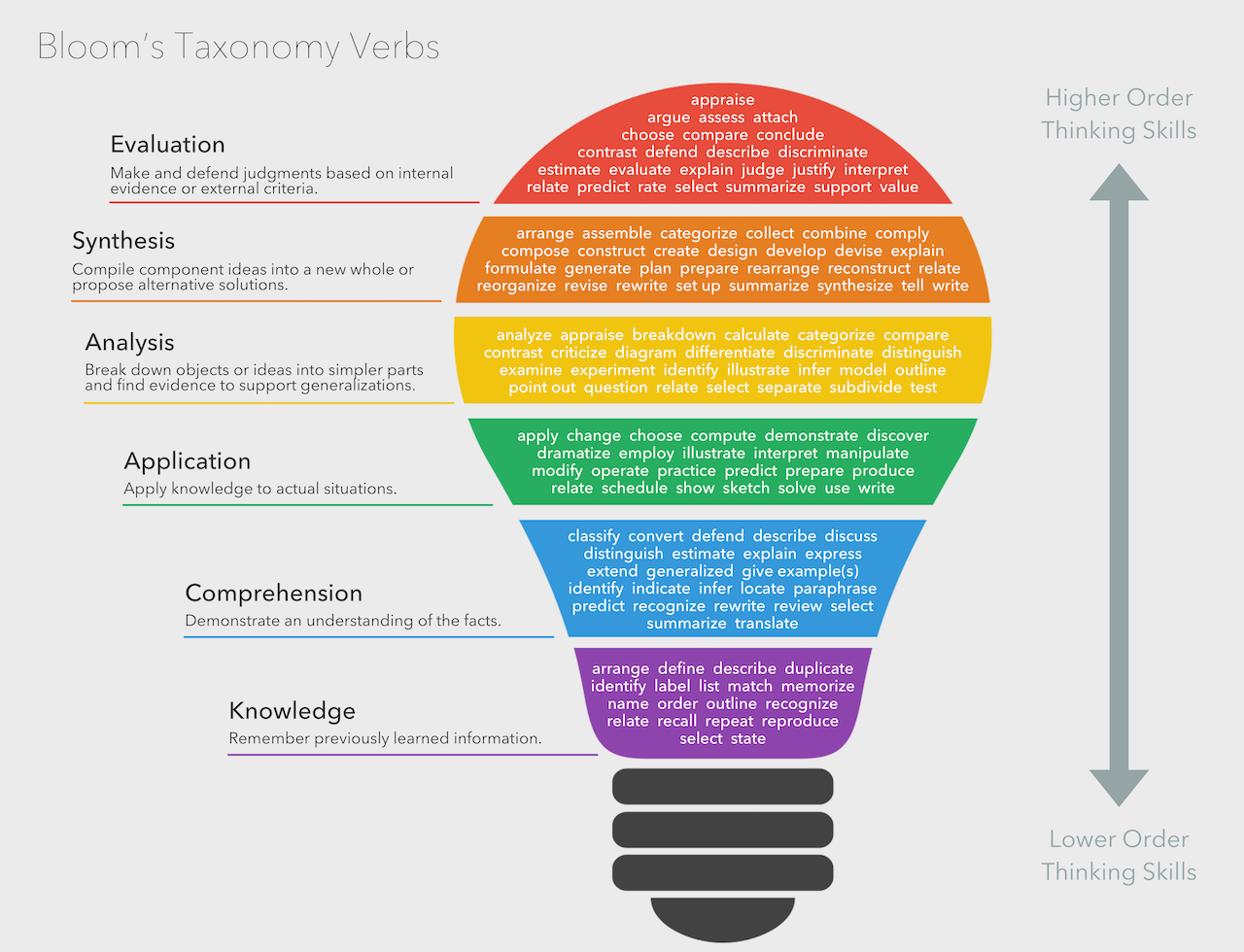
Bloomy Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs by Fractus Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Verbs in Bloom's Taxonomy are measurable and help instructors create quantifiable assignments and assessments. These verbs are helpful in planning lessons and curriculum.
AI will help you to:
Understanding Bloom's Taxonomy: Clear explanations of the different levels of Bloom's Taxonomy.
Generate Action Verbs: Suggest specific action verbs associated with each level of Bloom's Taxonomy, helping instructors create precise and measurable learning objectives.
Customizing Objectives for Students: Analyze student data and suggest customized learning objectives that meet varied learning styles and levels of understanding.
Providing Examples: Generate examples for learning objectives based on the subject area and educational goals, serving as a starting point for educators to refine as they see fit.
Facilitating Alignment: Aligning learning objectives with curriculum standards, assessments, and instructional strategies.
Feedback: Offers constructive feedback on drafted objectives, suggesting improvements and revisions to enhance clarity and effectiveness.
Sample Prompts for AI to Generate Course Level Objectives
Generate a list of course objectives for a [Subject/Topic] course aimed at [Target Audience]
What are some measurable learning objectives for a [Course Title] focused on [Key Theme/Concept]?"
Create detailed learning objectives for a lesson on [Specific Topic] that align with [Educational Standard or Framework]
What are three learning objectives for a unit on [Topic/Skill] for students in [Grade Level or Course Type]?
Suggest learning objectives using action verbs from Bloom's Taxonomy for a course on [Subject]."
How can I formulate objectives at the [Choose Level: Remembering, Understanding, Applying, etc.] level for a course about [Topic]?"
What learning objectives can I use to ensure my course on [Topic] is aligned with [State/National Standards]?"
Analyze the following draft objectives for clarity and effectiveness: [insert your draft objectives]. What improvements can you suggest?"
What revisions can enhance these learning objectives for a course on [Topic]? [insert your objectives]
AI provides solutions to create meaningful course objectives. Embracing AI in education saves time and empowers instructors to focus on delivering high-quality learning experiences. So why not take advantage of these advancements and elevate your course design today?
Unlock the Potential: The Power of Gamification in Education
Gamification is the use of game-design elements and principles in non-game environments.
What is Gamification?
Gamification is the use of game-design elements and principles in non-game environments. What this means to educators is that they can use gamification in educational settings.
What is Gamification Popular?
Gamification has become increasingly popular in recent years, with many companies and now educational institutions incorporating game-like features into their products. Adding gamification elements like badges or leaderboards increases user engagement and motivation. It makes routine tasks more enjoyable and rewarding, creating a sense of achievement and progress for users.
Gamification in Instructional Design
A popular trend in instructional design, gamification creates more interactivity and engagement for student users.
Let's explore the benefits of using gamification and some of the downsides.
Advantages:
Increases engagement - by adding gaming elements like badges, points, or leaderboards, learners are more motivated to participate and complete learning activities and increasing retention rates.
Making learning fun - can create a sense of competition and achievement, thus making learning less of a chore.
Disadvantages
Only for some students - some users will not be motivated to learn by rewards or competition.
Extrinsic motivation - users will focus on getting points or badges instead of genuine love for learning.
Unfair advantage - students who are good at playing games might do better than those who do not like gaming or are new to gaming.
Using Gamification Effectively in instructional design
Learning objectives are clear - What do you want your learners to learn? How will the game align with your learning objectives? Answering these questions will help you create games or incorporate gaming elements that make sense into your course content.
Don't overdo it - If you use too many gaming elements, it overwhelms the learner. Only use sparingly and without distracting from the course content.
Provide feedback: Learners need to know how they are progressing and what they need to do to improve. Ensure you provide regular feedback on their performance and progress toward their learning objectives.
Using Gamification in Education
Badges: Awarding badges for completing tasks or demonstrating mastery can motivate students to complete their work.
Leaderboards: Leaderboards ranks students again their peers, creating a sense of competition and motivating students to perform better.
Simulations/scenarios: Creating simulations or scenarios that allow students to apply their knowledge in a realistic setting can improve their understanding and retention of the material.
Role-playing games: allow students to explore complex social and cultural issues in a safe and engaging environment.
Interactive quizzes and games: Creating interactive quizzes and games that test student knowledge can help students reinforce their understanding of the material.
Gamification Tools
Booklet: Instructors can select question sets and game modes. Booklet generates a unique code for players to access the game. Once the game begins, the player can answer the various questions to win, keeping them engaged and motivated.
Brainscape: Looking to help students excel in their studies? Brainscape offers a seamless solution with its custom flashcard feature that turns learning into an engaging and rewarding experience. Create your personalized flashdeck today and make studying an enjoyable experience for students.
Quizalize: With this tool, you can easily craft questions about any topic you desire and then convert them into engaging gamified quizzes that everyone will enjoy!
Quizlet: This fantastic tool is free for instructors and students, making it an excellent resource for all. You can customize your quizzes and flashcards to suit your teaching style and create engaging games to keep your students interested and excited about learning.
Kahoot :This innovative tool allows you to effortlessly turn your quizzes into engaging games that keep your students interested and excited about learning. With its easy-to-use interface and customizable options, you can tailor your lessons to suit your teaching style and make the learning experience more enjoyable for everyone involved.
EdPuzzle: Teachers can effortlessly craft interactive video lessons that incorporate quizzes or other fun gaming elements. Whether you prefer to use your audio comments or come up with your questions, this innovative tool makes it easier than ever to keep students engaged and interested in the learning process.
In conclusion, gamification has the potential to be a highly effective tool in instructional design. Incorporating game elements into the course can improve the educational experience and make it more exciting and interactive for your students. However, it's important to use gamification effectively and for students to understand how they relate to the course's learning objectives. With these tips in mind, you can create course content that is both fun and effective.
I CREATED LEARNING OBJECTIVES, NOW WHAT?
After designing learning objectives, what activities will help achieve the learning objectives?
After designing learning objectives, what activities will help achieve the learning objectives? Depending on the subject area, there are various types of activities that a student can complete. A well-designed course module will have assignments, opportunities for discussion, collaboration, quizzes, exams, test, labs and practices exercises.
How Course Activities Help Student Learn
Assignments – helps students to understand the concepts and ideas presented in the course.
Discussion/Collaboration – help to facilitate communication between the students.
Quizzes/Tests/Exams/Labs/Practice Exercises – these assessments help identify any knowledge deficiencies and help students focus on the areas they need to review.
Course Activities
Using Bloom’s Taxonomy, Let’s go over the different activities you can design in your course.
Activities:
Code
Concept Mapping
Ice Breaker
Practice Quiz/Exam/Test
Read
Activities:
Discussion Forums
Debate
Oral Reports
Quiz, Exam, Test
Review (Play, Movie, Audio, Book, etcetera.)
Wikis
Activities:
Art Project
Group Problem Solving/Presentations/Reports
Interview
Journaling
Laboratory Experiments
Portfolios, Presentations
Simulations
Activities:
Brainstorming
Essay
Fieldwork
Group Reports/Debugging
Reflection
Activities:
Article Critique
Case Briefs
Case Studies
Document Analysis
Literature Review
Peer Editing/Review
Activities:
Audio Recording
Blogging
Gaming
Graphic Design
Individual Project
Video Creation
Web Design
Things to Consider when Designing Course Activities
Once you decide on the learning activities for your course module, you need to consider the following:
Learning Objectives – do the activities align with your with your learning objectives? Will the students achieve the skills you outlined in your objectives?
Relevancy – are the activities relevant to your course and the learning process? Do they promote learning and have an educational purpose?
Technical requirement – do students need to use specific software or create an online account to access certain tools? Are you familiar with the technology that you want your students to use? Are your students? Do not assume students are familiar with any technology you want to use in your course.
Designing your activities is an important step in your course module design process. By creating activities that align with your objectives, you not only make sure that your students have a successful learning outcome, but you also keep your students engaged and on task.
Do you agree with the activities that I used to match with Bloom’s Taxonomy? Why or why not? What activities do you like to use in your course? Please share it below!
ANATOMY OF A LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Learning Objectives are essential parts of any course module and course.
Designing your online course is not merely about creating content and sharing your passion for the subject you are teaching. You also need to make sure that what you are teaching is being learned. How do you ensure that this happens?
Learning Objectives are essential parts of any course module and course. Learning Objectives communicate to the student what they will learn after completing a learning module and be confident they will make measurable progress. They also help define what the instructor expects of them for the particular lesson and what the course accomplishes. Learning objectives in each of your course modules are good practice and make for a well-designed course.
When designing your learning objectives, you should ask yourself the following questions:
What will the students be learning?
What level of thinking will be used to process the content?
What observable student behavior will serve to show that the student has learned what they are supposed to?
What are the conditions (materials, time limits, etc.) that the student will expect to work under?
What is the level of mastery? What will satisfy you?
Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs by Fractus Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Created in 1956 by Psychologist Benjamin Bloom, Bloom’s Taxonomy is the most extensively used scale to demonstrate the level of expertise required for measurable student outcomes. Verbs in Bloom’s Taxonomy are measurable and help instructors create assignments and assessments that are quantifiable. These verbs are useful in planning lessons and curriculum.
There are six levels of knowledge in Bloom’s Taxonomy:
Knowledge -is measured by asking questions to see what they have remembered from a lesson—for example, a multiple-choice test.
Comprehension – determines their level of understanding by asking students to summarize, describe or discuss a topic.
Application – students apply what they have learned in real-life situations.
Analysis -students analyze a problem and provide supporting evidence as to how they solved the problem.
Synthesis – students merge information they have learned to provide new ideas and solutions.
Evaluation – students use the knowledge they have acquired to evaluate and apply their learning using evidence, observations, and other criteria determined by the student.
Bloom’s Taxonomy by Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Generic license.
Remember -is measured by asking questions to see what they have remembered from a lesson—for example, a multiple-choice test.
Understand – determines their level of understanding by asking students to summarize, describe or discuss a topic.
Apply – students apply what they have learned in real-life situations.
Analyze -students analyze a problem and provide supporting evidence as to how they solved the problem.
Evaluate – students use the knowledge they have acquired to evaluate and apply their learning using evidence, observations, and other criteria determined by the student
Create – students merge information they have learned to provide new ideas and solutions.
Let’s break it down!
Sample Objectives
Sample 1: Learning Objective (Text)
Students will be able to draw on Sketchpad the four life cycles of a butterfly after reading The Very Hungry Caterpillar.
Conditions – Sketchpad, reading The Very Hungry Caterpillar
Cognitive Process – draw (Remember) (Knowledge)
Content – life cycles of a butterfly
Observable Proving Behavior – drawing on Sketchpad the life cycles of a butterfly
Standard of Mastery – drawing the four life cycles of a butterfly
Sample 2: Learning Objective (Text)
After a lesson on Linear Algebra, students will be able to correctly solve at least 8 out of 10 algebra problems using Linear Algebra.
Conditions – lesson on Linear Algebra
Cognitive Process – solve (Apply) (Application)
Content – Linear Algebra
Observable Proving Behavior – correctly solve algebra problems using Linear Algebra
Standard of Mastery – at least 8 of 10 Linear Algebra problems
Sample 3: Learning Objective (Text)
Given the website, Linkedin.com and Chapter 4 in their textbook, students will create a Linkedin profile to effectively navigate the Linkedin interface and assess how Linkedin can be used to connect with peers and professional networking activities.
Conditions – Linkedin website, Chapter 4 of textbook
Cognitive Process – create (Create) (Synthesis)
Content – assess how Linkedin can be used to connect with peers and professional networking activities
Observable Proving Behavior – Linkedin profile
Standard of Mastery – effectively navigate the Linkedin profile
Objective Builder
Developed by the University of Central Florida , use the Objective Builder Tool and create your objectives with this easy-use tool!
While it can be a bit daunting creating learning objectives, correctly done objectives are the first step in creating a high-quality course module and instruction.
What difficulties have you encountered creating learning objectives? Hopefully, this post has provided helpful information! Please let me know what other topics you would like for me to discuss in the comments below. See you in the next post!