How Generative AI Can Enhance Accessibility in Teaching and Learning
Discover how Generative AI can transform accessibility in teaching and learning. In this video, we explore ways educators can use AI tools to create more inclusive learning environments.
As educators in this modern world, creating an inclusive learning environment should now be at the top of our list. Our goal should always be for all students to thrive.
Ensuring that course content, communication, and assessments are accessible can be time-consuming, especially for busy faculty.
That’s where generative AI can make a meaningful difference. When used thoughtfully, AI tools can help you design more inclusive and flexible learning experiences that meet diverse needs.
Below are ways AI can enhance accessibility in your courses without requiring advanced technical skills or extra tools.
Generate Alternative Text for Images
Alt text (alternative text) is important for learners who use screen readers. It describes images so that learners with visual impairments can access the same information.
How to use AI:
Upload or describe an image to tools like ChatGPT, Microsoft Copilot, or Canva’s AI assistant and ask for help to create a concise, descriptive alt text.
Prompt example:
“Write alt text for an image showing a student doing a math problem on a chalkboard"
Tip:
Keep AI-generated alt text concise and fact-based. Review it for accuracy and clarity before posting to your course.
Simplify Complex Texts for Readability
Some course required readings are written at very high reading levels, which can pose barriers for students with learning disabilities, English language learners, or cognitive differences.
How to use AI:
Summarize complex material using accessible language without losing meaning.
Prompt example:
“Summarize this 1000-word article for an audience reading at a 9th-grade level, keep key concepts intact.”
Use it for:
Reading guides
Lecture summaries
Study aids
Provide Transcripts and Captions
Audio and video content can be challenging for students who are deaf, hard of hearing, or prefer text-based study aids.
How AI helps:
AI transcription tools (like Otter.ai, or Zoom’s built-in AI assistant) can generate transcripts and captions automatically. You can then check them for accuracy before using in your course.
Bonus: Transcripts benefit all students by making it a searchable study material and aiding in comprehension for non-native speakers.
Generate Clearer Instructions and Rubrics
Ambiguous directions can disadvantage students who process information differently or rely on assistive technology.
How AI helps:
AI can rewrite your assignment instructions for clarity and consistency.
Prompt example:
“Rewrite these assignment directions to be clearer, more step-by-step, and easier to follow for students with ADHD.”
Create Inclusive Examples and Scenarios
Representation matters. AI can help you diversify the examples, names, and perspectives in your teaching materials, helping all students feel seen.
Prompt example:
“Generate a scenario about teamwork in healthcare using culturally diverse names and avoiding stereotypes.”
Always review outputs to ensure inclusivity and accuracy, but AI can speed up the brainstorming process.
Support for Neurodiverse Learners
AI tools can help students and instructors organize information, manage tasks, and summarize content. For example, learners with ADHD, dyslexia, or executive function challenges will learn more easily.
Examples:
Summarize discussion posts into key themes.
Turn long instructions into numbered steps.
Create visual outlines or mind maps using AI-powered design tools.
Instructors can use these strategies and but should also encourage students to use them responsibly.
Translate and Adapt Content for Multilingual Learners
AI translation tools (like DeepL or ChatGPT with multilingual support) can help make your materials more accessible for students who are non-native English speakers.
Prompt example:
“Translate this discussion question into Spanish and simplify it for an intermediate English learner.”
It’s not always perfect, so make sure to verify its accuracy, but it provides a valuable starting point for inclusion.
Conclusion
Generative AI isn’t a replacement for accessibility design. It should be as a support tool that makes inclusion easier to achieve. Integrating AI into your workflow can help you save time and also enhance the learning experience for all students.
Accessibility isn’t about compliance. Accessibility is about equity, empathy, and connection. And now, with the help of AI, creating inclusive learning environments has never been more possible.
Why Use Desktop Recordings? Intro to Clipchamp
Using desktop recording as an instructor can greatly enhance your teaching effectiveness and student engagement. Microsoft Clipchamp is an online video editor that simplifies video creation. Check out this helpful tutorial to learn how to use it!
Using desktop recording as an instructor can greatly enhance your teaching effectiveness and student engagement for several reasons:
Visual Learning: Desktop recordings allow you to record course content, software, or websites, making complex concepts easier to understand.
Accessibility: Recordings can be made available for students to review at their own pace. This is especially helpful for those who may need to revisit certain topics.
Engagement: Incorporating multimedia elements into your lessons can keep students more engaged. Interactive elements or real-time demonstrations can make learning more dynamic and engaging.
Fostering Community: Creating desktop recordings with your class can create a sense of community, as students can see you and hear your voice, making it possible to connect with you. It can also make the classroom experience feel more personal and supportive.
Support Diverse Learning Styles: Not all students learn in the same way. Some may excel with visual and auditory information, making recordings an excellent tool for accommodating different learning preferences.
Feedback and Improvement: Reviewing your recorded sessions can help you evaluate your teaching style and identify areas for improvement, allowing you to enhance your delivery for future classes.
Overall, desktop recording can be a valuable tool to supplement your teaching and provide a richer educational experience for your students!
Clipchamp
What is Clipchamp?
Microsoft Clipchamp is an online video editor that simplifies video creation. It offers intuitive tools that make it easy to create videos without requiring extensive technical skills. Users can combine videos, images, and audio. Once editing is complete, videos can be easily saved to your device. Unlike many other editors, Clipchamp operates in your browser without needing software downloads.
Pricing: FREE
Paid subscription (access to premium features): Monthly $11.99, Yearly $119.99
Clipchamp Tutorial
Accessing Clipchamp
Start by going to https://app.clipchamp.com/ Please note: You can only use Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge
2. Create an account or signup with your email
Recording your Video
Click on Create a new video
2. Select Record and Create
3. Select the type of recording you will be doing. Make sure to enable your microphone and camera.
4. Click on the red button to start recording. You also have the option of turning on Speaker Coach. This will analyze your recording's speech, including pace, pitch and use of filler words.
5. Choose what you want to record, you will see your current browsers tabs, windows you currently have opened or the option to record your entire screen
6. When you've finished your recording, simply click on either (1) Stop Sharing or the Stop button. You'll then be prompted to either (2) Save and Edit your recording or to redo it.
Please note: If you haven't upgraded your account, you'll need to (3) save the recording to your local hard drive. This means you'll need to either work on the same computer every time you want to work on your project or save the file to an external hard drive, allowing you to access it from any computer you use.
Editing your Video
You have a wide range of options to enhance your video, including:
Resizing, cropping, or trimming to perfect your video
Adding text, transitions, or selecting from a variety of templates to seamlessly integrate into your media
Incorporating video filters, images, or background music
Adding captions for improved accessibility and engagement
Explore these features to make your video stand out and check out the Clipchamp YouTube to find helpful videos that will show you how to use Clipchamp like a pro!
Exporting your Video
Once you’ve completed your recording, you can easily export your video and begin using it in your class right away!
In conclusion, incorporating desktop recordings into your teaching strategy can enhance the learning experience for both you and your students. With tools like Clipchamp, educators can create more engaging learning environments.
Desktop recording offers both flexibility and convenience. Whether you share introductory psychology insights or more advanced topics, using multimedia resources can lead to a more enriching learning experience. So, start recording and sharing your unique teaching style. Your students will thank you!
A Guide to Using Google NotebookLM for Course Design
Google NotebookLM is a powerful tool for organizing and developing course content and can enhance and fine-tune your existing ideas.
What is Google NotebookLM?
Google NotebookLM allows users to easily create, organize, and share notes. It acts like a virtual assistant that uses existing information to summarize details, clarify complex ideas, and generate relationships based on selected sources. It can handle various content types, including text, images, graphs, and diagrams.
Benefits of Using Google Notebook LM for Course Design
Organized Planning
Instructors can create separate notebooks for course outlines, reading materials, assessment plans, study guides, and course lectures. This organized structure simplifies the planning process and allows for easy navigation and access in the future.
Resource Compilation
It allows you to compile links, articles, videos, and other materials in one place. You can save links directly into your notebook, annotate them for future reference, and classify them according to topics.
Collaborate
It supports collaboration by allowing multiple users to edit and comment on notes in real time.
Easily Accessible
Since Google NotebookLM is cloud-based, you can access your notes anytime, anywhere, and on any device, allowing you to brainstorm ideas anywhere!
How to get started with Google NotebookLM
Let me walk you through how to start Google NotebookLM!
Creating a Notebook
Go to https://notebooklm.google.com/ and login with your Gmail account.
You will see your Google NotebookLM Dashboard with all the different notebooks you have created so far.
To create a new Notebook select "Create New"
Adding Content to your Notebook
It will prompt you to upload documents, google drive files, text, audio files, website links and YouTube videos. If you are not ready to do that, you can click on the X to close the window.
Make sure to name your Notebook.
Summarizing content using NotebookLM
Once you have uploaded all the content you want for the specific Notebook you created, you can use the "Chat" feature to ask questions about the different content. You can easily select the content you want to include by checking or unchecking the corresponding boxes next to each item. NotebookLM also offers you prompts to choose from, making it easier to develop your content. Please note: Content might not be accurate, so make sure to check for any mistakes.
How to Use Google Notebook LM for Course Design
Google NotebookLM is a powerful tool for organizing and developing course content and can enhance and fine-tune your existing ideas. You can use Google Notebook LM as a starting point for your course content. It will provide a solid foundation for you to build upon the ideas and suggestions it offers to make them even better and more tailored to your specific needs.
Create Course Objectives: create course or module objectives based on selected content. You can enter prompts like, “Create objectives for a module on [topic]” to get customized suggestions.
Develop Lesson Plans: outline the main concepts for each lesson. For instance, input, “Create a lesson plan for teaching [specific topic], including objectives, materials, and activities.”
Create Study Guides: use prompts like, “Create a study guide for [topic] that includes key concepts and questions.” NotebookLM can help summarize important information and develop study questions.
Create Discussion Prompts: generate discussion prompts based on content selected. You can input, “What are some engaging discussion prompts for [topic]?” to stimulate thoughtful discussions in class.
Create Rubrics and Criteria: determine what you will assess (e.g., projects, participation, etc.). Input requests along the lines of, “Create a rubric for assessing [specific project or assignment] that includes criteria for [aspects such as creativity, understanding, effort, etc.].” This will produce a structured assessment guide that you can further customize.
You can effectively use Google NotebookLM to streamline your course design process, enhance student engagement, and collaborate with others in the educational field! Happy designing!
Optimizing Learning Objectives with AI
With the increasing integration of AI (Artificial Intelligence) into the educational landscape, instructors can now use AI for content creation, such as developing clear learning objectives and assessments.
With the increasing integration of AI (Artificial Intelligence) into the educational landscape, instructors can now use AI for content creation, such as developing clear learning objectives and assessments. Well-defined learning objectives clarify expectations for students and ensure that assessments are closely aligned with those goals.
In this blog post, we'll take a look at some helpful AI tools for developing course objectives and walk you through the process of creating them.
Understanding Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives are important parts of any course. Learning Objectives communicate to students what the instructor expects and what the course accomplishes. Learning objectives are good practice and make for a well-designed course.
How Can I use AI in Creating Learning Objectives?
Alignment with Standards
Ensure learning objectives align with accreditation requirements or educational benchmarks. This helps maintain credibility and relevance in course offerings.
Feedback and Iteration
Provides suggestions for improving learning objectives based on student feedback or performance data. Continually improving course objectives helps them remain current and impactful.
Analyzing Learning Outcomes
Analyze existing course materials to identify important outcomes. By processing large volumes of data, AI can suggest relevant knowledge and skills that should be included in your objectives.
Generate Content
Generate initial drafts of learning objectives based on input from instructors. Instructors can focus more on refining content rather than starting from scratch.
AI Tools to Use to Create Learning Objectives
ChatGPT - AI chatbot that can generate human-like responses to different prompts
Google Gemini - Helps to write, plan and learn and responds with information it already knows or from other sources
Grammarly - Uses AI to enhance your writing and offers personalized guidance
Claude AI - Can generate human-like responses to text or image inputs.
Microsoft Copilot - Allows you to generate text or create images based on text prompts
Incorporating AI into Your Learning Objectives
To get started with using AI for creating course objectives, follow these steps:
Determine Course Themes: What is the primary focus of your course? What learning outcomes can students anticipate? For instance, if your course is in Environmental Science, consider whether your central theme revolves around sustainability.
Select the Appropriate Tool: Select one or more AI tools that best fit your needs. Take time to explore their features to see if they can assist you in aligning and generating objectives.
Draft Objectives: Use AI to generate preliminary course objectives. Make sure to refine the objectives with your insights and expertise.
Seek Feedback: Share your objectives with colleagues for feedback. AI can assist in analyzing this feedback to improve your objectives.
Align and Finalize: Ensure the objectives align with your teaching strategies and assessment methods before finalizing them.
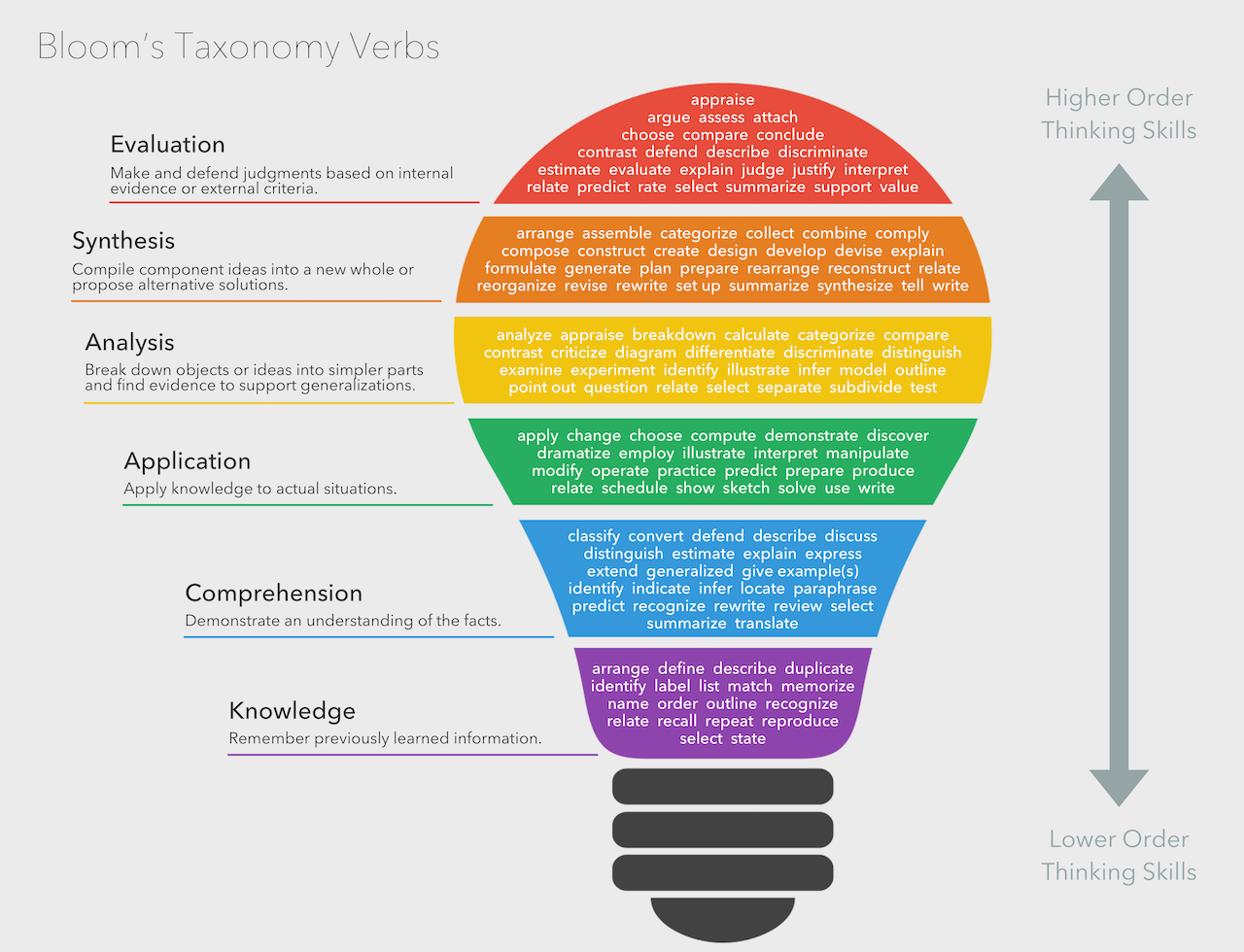
Bloomy Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs by Fractus Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Verbs in Bloom's Taxonomy are measurable and help instructors create quantifiable assignments and assessments. These verbs are helpful in planning lessons and curriculum.
AI will help you to:
Understanding Bloom's Taxonomy: Clear explanations of the different levels of Bloom's Taxonomy.
Generate Action Verbs: Suggest specific action verbs associated with each level of Bloom's Taxonomy, helping instructors create precise and measurable learning objectives.
Customizing Objectives for Students: Analyze student data and suggest customized learning objectives that meet varied learning styles and levels of understanding.
Providing Examples: Generate examples for learning objectives based on the subject area and educational goals, serving as a starting point for educators to refine as they see fit.
Facilitating Alignment: Aligning learning objectives with curriculum standards, assessments, and instructional strategies.
Feedback: Offers constructive feedback on drafted objectives, suggesting improvements and revisions to enhance clarity and effectiveness.
Sample Prompts for AI to Generate Course Level Objectives
Generate a list of course objectives for a [Subject/Topic] course aimed at [Target Audience]
What are some measurable learning objectives for a [Course Title] focused on [Key Theme/Concept]?"
Create detailed learning objectives for a lesson on [Specific Topic] that align with [Educational Standard or Framework]
What are three learning objectives for a unit on [Topic/Skill] for students in [Grade Level or Course Type]?
Suggest learning objectives using action verbs from Bloom's Taxonomy for a course on [Subject]."
How can I formulate objectives at the [Choose Level: Remembering, Understanding, Applying, etc.] level for a course about [Topic]?"
What learning objectives can I use to ensure my course on [Topic] is aligned with [State/National Standards]?"
Analyze the following draft objectives for clarity and effectiveness: [insert your draft objectives]. What improvements can you suggest?"
What revisions can enhance these learning objectives for a course on [Topic]? [insert your objectives]
AI provides solutions to create meaningful course objectives. Embracing AI in education saves time and empowers instructors to focus on delivering high-quality learning experiences. So why not take advantage of these advancements and elevate your course design today?
TYPOGRAPHY IN COURSE DESIGN
You encounter typography almost every day! Do you know what typography is?
You encounter typography almost every day! Do you know what typography is? Typography is how you arrange text and letters using spacing, different fonts, and different font sizes. You are using text and letters to create a story. You can use typography to convey various messages and create engaging and readable text. So why is this important for your online course? If you think about it, online course design is almost entirely using text, so why would you not want to use text to create a course that is both readable and visually appealing?
Reasons why you should use Typography in your course:
Optimizes readability – using good typography creates a visual hierarchy. It lets the reader know which elements are essential and how they relate to the other text in your course content. One example of this is using headers. Headers established the main points of each page of content. Examples of headings you can use are H1, H2, H3, and H4.
Creates accessible content: Did you know that you can make your content more accessible with learners who have poor vision depending on the font you choose? Many learners have learning disabilities such as poor vision, dyslexia, or aphasia and need to have course content be as accessible as possible. For example, make sure that all font letters you use are easily distinguishable since many fonts have letters that look alike.
Creates a memorable experience: By using good typography, you create a good experience for your learner. You hold their attention and thereby helping them to easily read and remember your course content and stay focused and engaged in the course.
Basics of Typography
Typography has the following elements that you need to understand to use in your course:
Typeface
Not to be confused with font, it is the style that makes up the font. In contrast, the font is how you graphically render a text character.
There are three types of typeface, (1) serif (2) san-serif and (3) decorative:
In your course, you will not want to use all three simultaneously. You will want to use two fonts at most to keep it clean and easy to read.
Contrast
You create contrast when you emphasize certain text and not the other. One example of this would be using headers or images that has text. You can use text size or color to signify which course information grabs the learner’s attention.
Example 1
Example 2
Hierarchy
Lets your learners understand what they need to read first and how content is organized. Headers allow you to manage your content using different heading:
Whitespace
Also called “negative space.” Whitespace ensures the content is not overwhelming and created when you chunk your content or create other groupings. It makes more visually appealing content by not allowing too much clutter to appear on the page.
Consistency
Having consistent fonts and hierarchy for your course content is vital. If you use too many fonts or hierarchy in one page of content and not in the other might lead to a confusing and even disordered look of your course.
Example of content having too many fonts
Color
The color you use for your content is important. One reason is you might have learners who are colorblind. You can quickly check for color contrast using this online contrast checker.
Alignment
This is how your text or images align with other elements in your course content. You want to keep this as consistent as you can. For example, you might want to place a course banner on the top center of your page or any images you use on the left of the page before the paragraph begins.
Now that you understand the basic principles of typography, I hope they will help you when designing your course content. Comment below if you are using typography principles in your course or any tips you would like to share!
IMPORTANCE OF A MODULE OVERVIEW
There is excitement, context, or curiosity created to stimulates students' interest in a topic.
When going to a bookstore or library, what is the first thing most people look at when they pick up a book that interests them? Is it the table of contents? The author or maybe the book summary? If the answer is the book summary, it also explains the importance of having a course module overview.
The book summary convinces people to read a book and creates a first impression on the reader, just like a course module overview creates that initial reaction from your students. That is why a course overview is an integral part of a course module. Before a student begins their module, described as a lesson, chapter, unit, or segment of instruction, the student should be introduced to the content and the module’s purpose.
The module overview summarizes what they will learn in the module, how it may build on previously learned information, and its relation to the course. It also helps students remember the main ideas, relevant information, and material covered in the course module.
Let’s break it down
Sample Module Overviews
Sample 1: Module Overview(Text)
Without even realizing it, we use the principles of psychology every day. Have we ever grounded a child for being disobedient? We are using negative punishment, a type of operant conditioning. Psychology studies behavior, emotion, and cognition. Psychologists work to understand people better and how and why we act in certain situations. In this module, we will review the history of psychology as a discipline. We will also discuss the variety of specialty areas in Psychology and the five fundamental goals of Psychology.
[ how it relates to the course ] Without even realizing it, we use the principles of psychology every day. Have we ever grounded a child for being disobedient? We are using negative punishment, a type of operant conditioning. Psychology studies behavior, emotion, and cognition. Psychologists work to understand people better and how and why we act in certain situations.
[ main ideas, relevant information, and material covered in the course module] In this module, we will review the history of psychology as a discipline. We will also discuss the variety of specialty areas in Psychology and the five fundamental goals of Psychology.
Sample 2: Module Overview(Text)
[ how it relates to the course ] Our previous lesson covered an introduction to chemistry and how it is found everywhere, not just in a lab setting. Drinking soda or having your plant hit sunlight, there is a chemical process happening. This module will cover the chemistry of life. Did you know that fruit is a rich source of biological macromolecules or large molecules needed for life?
[ main ideas, relevant information, and material covered in the course module] Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and phosphorus can be found in living things and are the critical building blocks of life. We will discuss the importance of these building blocks, their unique properties, and how their interactions with other atoms help shape life molecules.
A module overview can compare to presenting a lecture or lesson in a face to face class. You do not just start lecturing about the lesson. There is excitement, context, or curiosity created to stimulate students’ interest in a topic and connect new information to previous information. So be creative in the module overview!
Please let me know what other topics you would like for me to discuss in the comments below. See you in the next post and please share with others if you find this information useful!
MAKING COURSE CONTENT EASY TO READ
Have you have ever visited a web page and can't find what you are looking for on the page.
Have you have ever visited a web page and can’t find what you are looking for on the page. Many users get frustrated right away when they can’t locate what they need on the page. In an online course, users feel the same way. If you create a page that is all text or has a very long scroll, your students will not be excited about the content. They will find it tedious to read through every line of text or paragraph to figure out the content. Creating an easy-to-read page is easy to do. You will want to make sure your content has the following:
Heading/Subheadings– helps to organize the content.
Chunking – don’t group too much text together, make sure you create short logical paragraphs.
Transitions – make sure your content transitions easily from one idea to another.
Images – enhances your message and keep students interested.
Bullets/Numbered Lists – helps students visually see essential information.
White Space – makes sure that the content is not overwhelming and is created when you chunk your content or create other groupings.
Let’s look at an example and break down the different elements.
Headers/Subheadings
Makes content easy to locate and creates a visually appealing page. Main header will use <h1> tags, while subheadings will use <h2>, <h3>, <h4> tags.
Chunking
Creating short paragraphs of information makes the content less intimidating and easier to read.
Transitions
Transitions help readers understand how the content is connected. If you create several paragraphs of content, make sure to incorporate transitional statements like:
In addition
In particular
For example
In fact
For this purpose
In conclusion
Images
Images reinforce the message. Use when appropriate.
Bullets/Numbered Lists
Helps students to locate key points and sort items.
White Space
Creates a visually appealing page and content. Content is not overwhelming and easier to understand.
In conclusion, creating clear and intuitive content and avoiding a cluttered page will facilitate learning, help students understand their lesson, and quickly locate the information they need.
I hope you enjoyed reading this post! Please post below how you design your course content and other methods you use to help students understand the course content.
MODULAR COURSE DESIGN
A well-designed course makes students perform the right choices and draw the correct conclusions about how they are supposed to navigate your course.
Have you ever visited a website and were confused about the website layout? Did you have trouble locating the information you were looking for on the website? Did you not understand how to navigate the website and were left feeling frustrated? Course design is very similar to website design. You want the user to have the best possible experience, locate the information/resources, and understand your course or website’s flow. A well-designed course makes students perform the right choices and draw the correct conclusions about how they are supposed to navigate your course. Using modular course design will help achieve this goal.
Why Course Modules?
Creating course modules in your online course is best practice. By dividing your information into smaller, more manageable segments of information and presenting it in a linear format, there is less likelihood that your student will have problems following your course structure and navigation. Designing your course in this approach is considered modular course design. In other words, you want to use segments of information that uses a logical path to teach your class. Each module is a self-contained block of information.
A book, for example, uses a modular approach. The chapters in the book would be considered modules. Each module is unique and has content related to only that specific module. So just like a book, you want to create content that makes sense for those modules. For example, most instructors create modules titled ” Week 1, Week 2, so on and so forth” This approach lets the student know that the course is structured by the current week. You don’t want to title one module “Lesson 1” and then your next module “Chapter 2”, where there is no consistency.
Components of a Course Module
Once you decide on the naming convention of your modules, what elements will make up a module? It all depends on your teaching style, but recommended components to include will be the following:
Banner (Optional)
Module Overview – overview of your course module.
Learning Objectives – what does your module hope to accomplish?
Lecture – made up of text, PPTs (PowerPoint), PDFs, video, audio, or external resource.
Assignments – help students to understand the concepts and ideas presented in the course.
Quizzes/Exams/Test/Labs -these assessments help identify any knowledge deficiencies and help students focus on the areas they need to review.
Practice Exercises (Quizzes, Labs, etc.) – help students review or practice skills and knowledge acquired.
Discussion – help to facilitate communication between the students.
Feedback – in the form of a survey or other manner that allows students to give feedback on their course progress so far. Feedback from your students can help you understand if there are any course deficiencies.
Supplemental Resources (Optional) – links to websites, publisher content, or other external resources that further enhance students’ learning. You can make this an optional activity for the student.
Sample Modular Course Design Template
Sample modular course design structure of first two weeks of a course
Each module should be created in a logical sequence, although every module might not look the same. You might include some components in a module but not in others. What is essential is to be consistent.
Modular course design helps to design a successful online course. Once you carefully develop one module, it not only creates a template for your other course modules, you can also visually see how your modules relate to your course syllabus and course outcomes. Additionally, it enables you to transfer over content more easily from one part of the class to another or to another Learning Management System (LMS).
What are your thoughts about using modular course design for your course? Do you think your students benefit more from this type of course design? Let me know in the comments below!
I CREATED LEARNING OBJECTIVES, NOW WHAT?
After designing learning objectives, what activities will help achieve the learning objectives?
After designing learning objectives, what activities will help achieve the learning objectives? Depending on the subject area, there are various types of activities that a student can complete. A well-designed course module will have assignments, opportunities for discussion, collaboration, quizzes, exams, test, labs and practices exercises.
How Course Activities Help Student Learn
Assignments – helps students to understand the concepts and ideas presented in the course.
Discussion/Collaboration – help to facilitate communication between the students.
Quizzes/Tests/Exams/Labs/Practice Exercises – these assessments help identify any knowledge deficiencies and help students focus on the areas they need to review.
Course Activities
Using Bloom’s Taxonomy, Let’s go over the different activities you can design in your course.
Activities:
Code
Concept Mapping
Ice Breaker
Practice Quiz/Exam/Test
Read
Activities:
Discussion Forums
Debate
Oral Reports
Quiz, Exam, Test
Review (Play, Movie, Audio, Book, etcetera.)
Wikis
Activities:
Art Project
Group Problem Solving/Presentations/Reports
Interview
Journaling
Laboratory Experiments
Portfolios, Presentations
Simulations
Activities:
Brainstorming
Essay
Fieldwork
Group Reports/Debugging
Reflection
Activities:
Article Critique
Case Briefs
Case Studies
Document Analysis
Literature Review
Peer Editing/Review
Activities:
Audio Recording
Blogging
Gaming
Graphic Design
Individual Project
Video Creation
Web Design
Things to Consider when Designing Course Activities
Once you decide on the learning activities for your course module, you need to consider the following:
Learning Objectives – do the activities align with your with your learning objectives? Will the students achieve the skills you outlined in your objectives?
Relevancy – are the activities relevant to your course and the learning process? Do they promote learning and have an educational purpose?
Technical requirement – do students need to use specific software or create an online account to access certain tools? Are you familiar with the technology that you want your students to use? Are your students? Do not assume students are familiar with any technology you want to use in your course.
Designing your activities is an important step in your course module design process. By creating activities that align with your objectives, you not only make sure that your students have a successful learning outcome, but you also keep your students engaged and on task.
Do you agree with the activities that I used to match with Bloom’s Taxonomy? Why or why not? What activities do you like to use in your course? Please share it below!